The Symphony of Automation: AI in Smart Warehouses
- Tretyak
- Mar 12
- 3 min read

The modern warehouse is no longer a static repository but a dynamic, interconnected ecosystem. AI is the conductor of this symphony, orchestrating a seamless flow of goods through automation, intelligence, and precision.
A Detailed Exploration of AI's Role in Warehouse Automation:
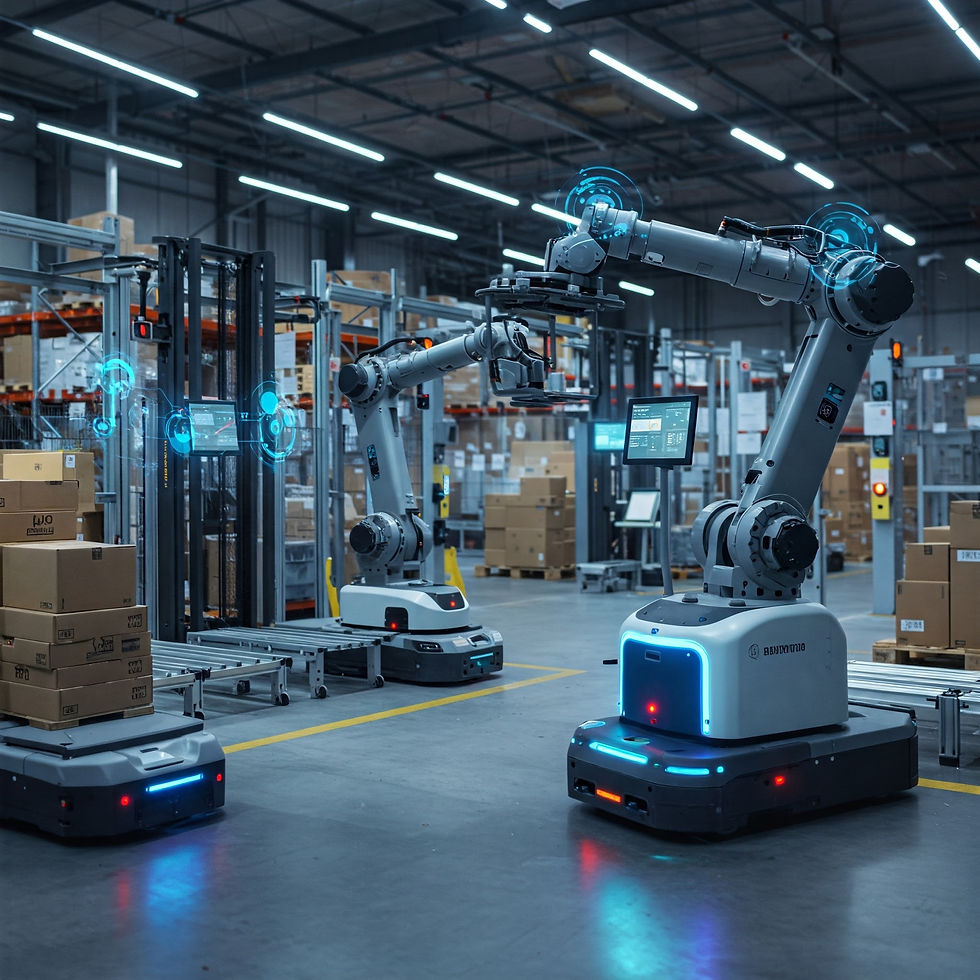
Advanced Robotics: The Choreographed Movement of Autonomous Systems:
Beyond Basic AGVs: Modern AMRs utilize sophisticated sensor suites (LiDAR, cameras, ultrasonic sensors) and advanced path-planning algorithms. This allows them to navigate complex, dynamic environments, avoid obstacles, and adapt to changes in real-time.
Collaborative Robots (Cobots): Cobots work alongside human employees, assisting with repetitive or physically demanding tasks. AI enables cobots to understand human intentions and movements, ensuring safe and efficient collaboration.
Robotic Picking Arms: AI-powered robotic arms with advanced grippers can handle a wide range of items, from delicate electronics to heavy packages. Machine learning algorithms enable them to learn and adapt to different object shapes and sizes.
Drone Integration: Drones are being integrated into warehouse operations for inventory scanning, locating misplaced items, and even transporting small packages within the facility. AI enables drones to navigate autonomously and perform these tasks with precision.
Intelligent Inventory Management: The Data-Driven Ecosystem:
Real-Time Inventory Visibility: AI-powered systems track inventory in real-time using RFID tags, barcodes, and computer vision. This provides complete visibility into stock levels, locations, and movements.
Demand Forecasting and Predictive Analytics: AI algorithms analyze historical sales data, seasonal trends, and external factors (e.g., weather, market events) to predict future demand with high accuracy. This enables warehouses to optimize inventory levels, minimize stockouts, and reduce holding costs.
Dynamic Slotting and Storage Optimization: AI algorithms analyze product velocity, size, and weight to optimize storage locations. This minimizes travel time for robots and human pickers, improving overall efficiency.
Automated Replenishment: AI-powered systems can automatically trigger replenishment orders when stock levels fall below a certain threshold, ensuring that products are always available.
Automated Picking and Packing: The Precision of AI Vision and Manipulation:
Computer Vision and Object Recognition: AI-powered vision systems can identify and locate items with high accuracy, even in cluttered environments. Deep learning algorithms enable them to recognize different product shapes, sizes, and packaging materials.
Automated Packing and Labeling: AI-powered systems can automate the packing and labeling process, ensuring that orders are fulfilled correctly and efficiently. This reduces human error and increases throughput.
Quality Control: AI vision systems can also be used for quality control, inspecting products for defects and ensuring that only high-quality items are shipped to customers.
Smart Sorting and Distribution: The Orchestrated Flow of Goods:
Automated Sortation Systems: AI-powered sortation systems can quickly and accurately direct items to their designated locations, based on destination, product type, or other criteria.
Optimized Loading and Unloading: AI algorithms can optimize loading and unloading operations, minimizing delays and ensuring that shipments are dispatched on time.
Real-Time Tracking and Traceability: AI-powered systems provide real-time tracking and traceability of goods throughout the warehouse and supply chain. This enhances visibility and enables proactive problem-solving.
Data-Driven Optimization and Continuous Improvement:
Sensor Networks and IoT Integration: Sensor networks and IoT devices provide a constant stream of data about warehouse activity, including temperature, humidity, and equipment performance.
Data Analytics and Machine Learning: AI algorithms analyze this data to identify bottlenecks, optimize workflows, and improve overall efficiency.
Digital Twins: Digital twins are virtual representations of the warehouse that can be used to simulate and optimize operations. AI-powered simulations can be used to test different scenarios and identify potential improvements.
Predictive Maintenance: AI algorithms analyze sensor data to predict equipment failures, enabling proactive maintenance and minimizing downtime.
In essence: AI in warehouse automation is not just about automating tasks; it's about creating a self-optimizing, intelligent ecosystem. It's about transforming warehouses into smart hubs that can adapt to changing conditions, anticipate future needs, and deliver exceptional customer experiences.






























































































Comments